The Sun has fueled life on Earth for billions of years. It provides warmth, light, and stability in our solar system. But what would happen if the Sun exploded? Could Earth and humanity survive a disaster like this? Let us explore this fascinating “what-if” scenario. We will look at how the Sun may change over time and what it could mean for everyone on Earth.
The Life Cycle of Our Sun
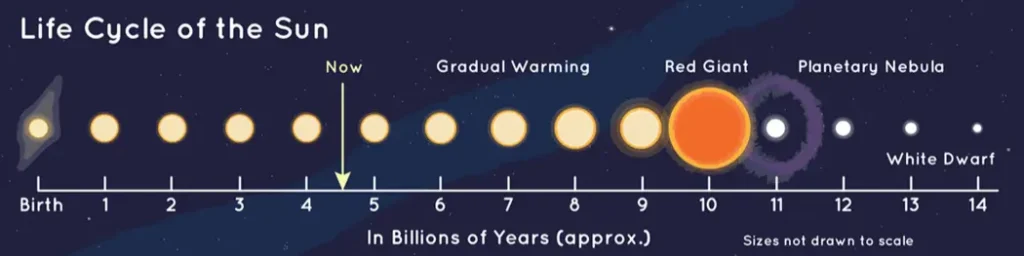
Like all stars, our Sun goes through a life cycle — from birth to death. Each stage reveals something important about its life.
The Birth of a Star: From Gas and Dust
Our Sun, like all stars, was not built to last forever. Stars have life cycles. They are born from giant clouds of gas and dust. Gravity pulls this material together and creates young stars. Once they ignite, they enter a stable phase. They burn fuel to produce energy and light. Over time, they begin to exhaust their fuel. They slowly age and prepare for their next transformation.
The Main Sequence: A Stable Phase
Right now, our Sun is currently in the middle of its main sequence phase. This is the longest phase in a star’s life. In this stage, it constantly burns hydrogen in its core. This process generates the energy that fuels our solar system. But one day, billions of years from now, that fuel will run out. Then, the Sun will enter its final stages of life.
Supernova or Not? The Sun’s Final Transformation
When people ask, “what would happen if the Sun exploded,” they imagine something like a supernova. A supernova is a bright and powerful explosion that occurs at the end of a star’s life. At its peak, this explosion can shine as brightly as an entire galaxy. It releases as much energy in just a few seconds as our Sun would produce over its entire lifetime. You can think of a supernova like bursting a balloon.
But here’s the truth: the Sun isn’t big enough to end its life with a huge explosion. When our sun dies, it will happen slowly, much like when you gradually let the air out of a balloon. It will transform dramatically, but it will not explode like a supernova.
What Will Happen When the Sun Dies?
1. The Red Giant Phase: A Fiery Expansion
In about 5 billion years, the Sun will run out of its hydrogen fuel. When that happens, it will expand into what astronomers call a “red giant”. It will get so big, that it will eat Mercury, Venus and even Earth.
If somehow Earth survives this first expansion, it will be burned. Surface temperatures will rise above 2,000 degrees Celsius (3,600 degrees Fahrenheit). The oceans will boil away, and the atmosphere will be stripped. The surface will become barren and lifeless.
2. The Planetary Nebula: A Last Glow
When the sun is a red giant, it will be big and puffy. It will shed its outer layers. This will create a beautiful shell of glowing gas known as a “planetary nebula”. This beautiful display will not be visible to us because life as we know it will not exist anymore. This phase will last for several thousand years.
3. The White Dwarf Phase: A Small, Dense Remnant
After the planetary nebula forms, the remaining core of the Sun will shrink over time. Eventually, it will become what we call a “white dwarf”.
A white dwarf is the core of a dead star. They are super heavy. They weigh almost as much as the Sun, but they are only the size of Earth. A teaspoon of a white dwarf would weigh about 6,000 kilograms. This weight is equal to that of an adult elephant!
When the sun is a white dwarf, most of the solar system will still be around. Mercury, Venus, and Earth will be gone. However, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune will still be here. They will continue to orbit the Sun. The asteroid belt, Kuiper Belt, and dwarf planets like Pluto will also remain.
4. The Black Dwarf: A Final, Cold State
The white dwarf will be small, so it will not produce much light. Since it will not have any fuel to give it energy, it will also get colder and colder over time. Over billions of years, it will eventually become a cold, dark object known as a “black dwarf”.
A black dwarf is basically a white dwarf that has cooled down. At this point, it no longer produces significant heat or light. This cooling process will take longer than the current age of the universe, which is about 13.8 billion years. As a result, no black dwarfs are believed to exist yet. However, the Sun will theoretically become a black dwarf. This will happen in the distant future. By then, the solar system will have changed significantly from what we know today.
So, what will happen to the Sun when it dies? First, it will become a red giant. Then, it will transform into a white dwarf. Finally, it will turn into a black dwarf. This process will not be an “explosion”. Instead, it will be a gradual transition.
What Will Happen to Earth and Humans When the Sun Dies?
When the Sun turns into a red giant and sheds its outer layers, Earth’s fate will be sealed. Let us explore a few likely outcomes:
1. Extreme Heat: As the Sun expands, Earth will experience a huge rise in temperature. The heat will evaporate the oceans, and the atmosphere will be stripped away. This will leave Earth barren and dry.
2. Cosmic Darkness: Once the Sun becomes a white dwarf, it will no longer shine as brightly. This will cause the solar system to fall into darkness. Without the Sun’s energy, temperatures across Earth would drop drastically. Within weeks, the surface would turn to ice, and life on the surface would be nearly impossible.
3. Surviving the Cold: Could humans survive if the Sun died? Well, Humans might create technology to live in artificial habitats. They could also find energy sources deep underground. But without the Sun, survival would be extremely difficult. Plants, animals, and humans all rely on the Sun’s warmth and light. In the deep cold of space, life would face extreme challenges. Even with technology, survival would be extremely tough.
What Will Happen to the Planets When the Sun Dies?
Each planet in the solar system will lose the Sun’s gravitational pull. This will cause their orbits to become unstable. Some planets may drift away into the emptiness of space. Others might continue to circle the faint white dwarf. Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, and planets beyond will continue to exist. But without sunlight, their environments will change drastically.
How Likely is a Sudden Solar Explosion?
While it is interesting to imagine a sudden explosion of the Sun, the reality is much less dramatic. Stars like the Sun do not explode as supernovae because they lack the necessary mass. Instead, they expand, lose material, and fade away. A true ‘explosion’ scenario is not likely to happen for our Sun.
Massive stars in the galaxy sometimes go supernova. These explosions send shockwaves that can impact nearby stars and planets. Fortunately, our Sun is stable, and Earth is safe from any sudden, explosive end.
Interesting Fact: Why Are Not All Stars Explosive?
Stars have a variety of fates based on their size. The Sun is a medium-sized star, which means it will become a red giant, then a white dwarf. Larger stars have masses at least eight times that of the Sun. They have enough gravitational energy to explode as supernovae. These explosions are rare. However, they create heavy elements and help to make new stars and planets in the galaxy. So, in a way, our Sun’s peaceful ending will be a unique type of transformation. It will be gentler than the dramatic endings of more massive stars.
Final Thoughts: A Dying Sun and Humanity’s Future
So, what will happen if the Sun explodes? The truth is, it will not explode, at least not like a supernova. The sun will become a red giant and then a white dwarf over billions of years. This white dwarf will gradually cool and fade, eventually becoming a black dwarf. But when the Sun dies and transforms, Earth will face its own end. Humanity will need to find new places to survive. Space exploration and the search for habitable planets will likely become essential long before our Sun’s red giant phase.
Imagining the end of the Sun can feel frightening, but it also reminds us of our cosmic journey. Stars are born, live vibrant lives, and pass on, much like life itself. And who knows? Maybe one day, humanity will watch the Sun’s transformation from the safety of a distant star system.
Until then, our Sun continues to shine and nurture life on Earth. Now, when you look up at the Sun, you will appreciate the incredible journey it will undertake. In billions of years, it will close a chapter of life in our solar system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Will our Sun explode like a supernova?
No, our Sun will not go supernova when it dies. A supernova is a violent explosion that happens only in massive stars. These are usually stars that are at least eight times more massive than the Sun. Massive stars have enough mass to create the extreme pressure in their cores. This pressure is needed for them to explode in a supernova at the end of their life cycles.
When our Sun nears the end of its life, it will expand into a red giant. It will shed its outer layers, creating a glowing shell of gas called a planetary nebula. At that time only the core of the sun will remain. The core will cool and shrink into a white dwarf. A white dwarf is a dense, Earth-sized object left behind after a star has died. It gradually fades over billions of years.
So, while a supernova might sound dramatic, the Sun’s end will be a quieter transformation. However, it will still change our solar system.
How long would we have if the Sun exploded?
If the Sun were to explode suddenly, we would feel its effects quickly. However, this scenario is very unlikely and not possible for a star like ours. That said, let us discuss the theoretical consequences:
1. Light and Heat: Light from the Sun takes about 8 minutes to reach Earth. This means we would have 8 more minutes of sunlight before everything went dark. After that, we would be in complete darkness, with no light or heat reaching Earth.
2. Shockwave: If an explosion somehow sent a shockwave our way, it would move at nearly the speed of light. This means it would also take around 8 minutes to reach us. By the time the shockwave arrived, it could cause catastrophic effects. It might strip away the atmosphere, oceans, and any remaining life on our planet.
3. Temperature Drop: Without sunlight, Earth would start cooling immediately. Within days, temperatures would plunge below freezing. In a year, Earth’s surface temperature could drop to -73°C (-100°F) or lower.
4. Neutrinos: In addition to light, a supernova would also release a huge number of neutrinos. Neutrinos are nearly massless particles. They travel at nearly the speed of light and would reach Earth in about 8 minutes as well. Neutrinos interact very weakly with matter. However, a large enough burst could have some effects. But these effects would be minor compared to other impacts.
5. Long-Term Impact: Without the Sun’s gravitational pull, Earth and other planets would drift into space. Life as we know it would become unsustainable within weeks or months. This includes even organisms living in deep-sea vents or underground.
Fortunately, the Sun does not have enough mass to explode in a supernova. So, this scenario is more theoretical than realistic!
What if the Sun disappeared for one second?
If the Sun disappeared for just one second, this is what would happen:
1. Loss of Light: Since it takes 8 minutes and 20 seconds for light from the Sun to reach Earth, we would not notice the darkness immediately. But after this delay, Earth would go dark for one second before the Sun’s light came back.
2. Gravity Effect: The Sun’s gravitational pull keeps Earth and the other planets in orbit. If the Sun vanished completely for a second, its gravitational pull would stop. As a result, Earth would move a little off its path. When the Sun reappeared, Earth would be pulled back. Even this small change could change our orbit a little, but it would not lead to an immediate disaster.
3. Temperature: In just a single second, Earth’s temperature would not change much. This is because losing heat takes time. The brief absence would not impact our climate.
4. Life on Earth: This one-second disappearance would likely go unnoticed by life on Earth. While our orbit might change a tiny bit, it would not cause any lasting effects for us.
So, if the Sun disappeared for one second, it would be an interesting and strange event. However, it would not significantly affect life on Earth. In short, we would have a brief interruption in sunlight and gravitational pull. But there would be almost no lasting impact!




